User Area
Software Release History - Version 20
New Facilities and Improvements
in LUSAS Version 20.0
V20.0-5 made available for download on 14 August 2024
This is a minor
update release that provides an updated Masonry Bridge Wizard that was
released with version 21.1
V20.0-4 made available for download on 12 July 2023
This is an error
fix release.
V20.0-3 made available for download on 26 June 2023
This is an error
fix release.
V20.0-2 made available for download on 8 March 2023
This is an error
fix release.
V20.0-1 made available for download on 9
February 2023
This is an error
fix release.
V20.0-0 made available for download on 28 November 2022
This is a major release
of new facilitites, enhancements and change requests
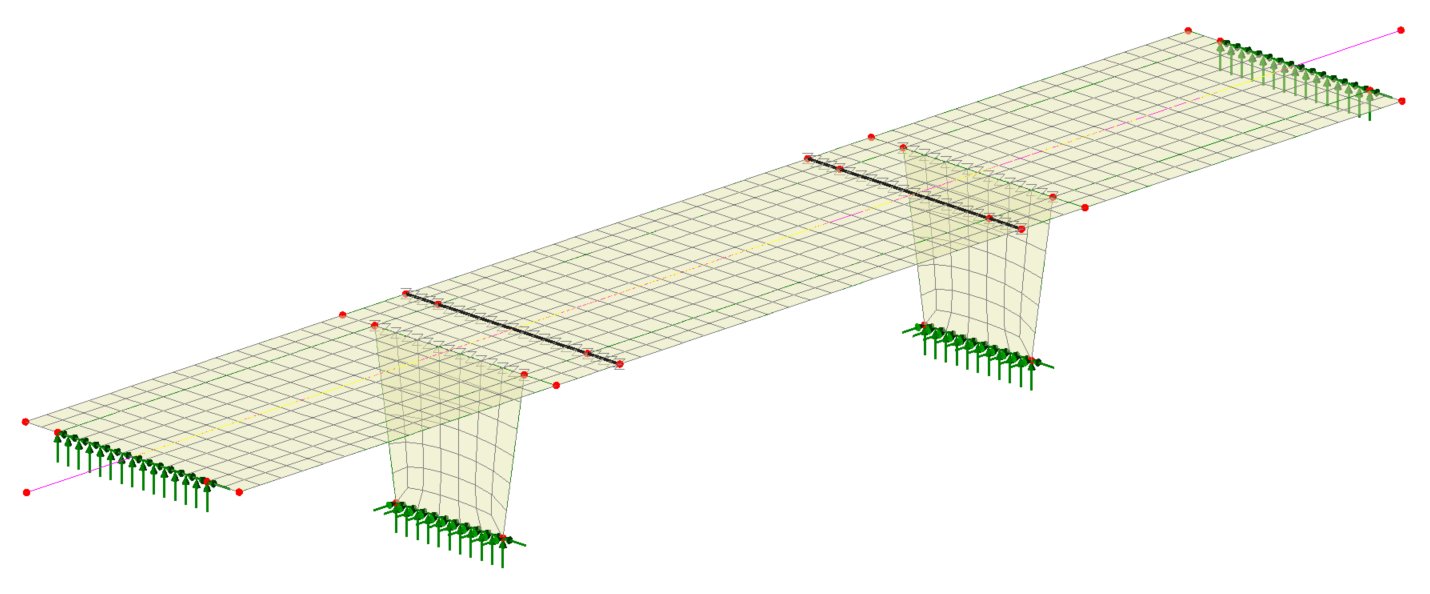
New software option: Masonry Bridge Wizard
- The new
Masonry Bridge Wizard software option generates 2D or 3D continuum models of single and multi-span bridges, including piers and abutments, with or without a skew, using linear or nonlinear materials.
Common features are grouped and named to allow for easy
manipulation of the model, or selective viewing of results. Optional library-based train loading can be defined within the wizard. Road and rail traffic loading to supported design codes can be assigned from within Modeller.
New Grasshopper plugin
For version 20 we partnered with Geometry Gym
to allow LUSAS “components” to be accessed from
Grasshopper - a visual programming language and environment which runs
within Rhino. It provided the means to:
- Interact directly with Grasshopper
parametric models. Make parametric changes and recreate LUSAS
models quickly using the “bake to LUSAS” function
- Transfer sophisticated Rhino line
and surface geometries reliably from Grasshopper to LUSAS,
including nurb lines and surfaces.
- The initial
release of this plug-in version was free.
We have since launched our own LUSAS-authored
plugin for Grasshopper.
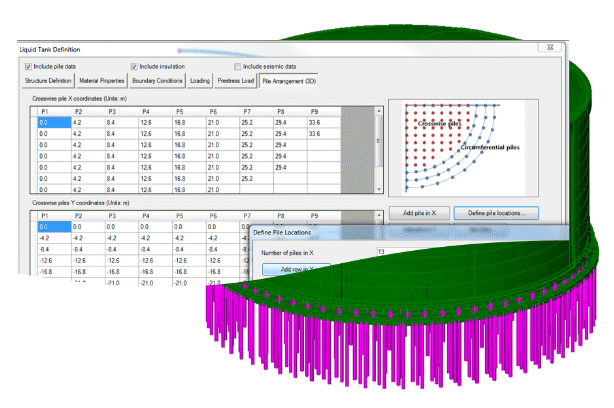
Updated LNG Tank System
Developments to the LNG
Tank System since Version 19.1 that are available for use when
running the LNG Tank System in Version 20.0 include:
- Modelling of elevated tanks
including isolator, pedestals, with raft and optionally
piles.
- Automatic creation of piled
foundations for above ground tanks Spillage (thermal)
analysis.
- Wind loading to ASCE (USA) and
GB50010 (China) codes.
- RC design to GB50009 (China)
Comprehensive design check reports in spreadsheets.
- A range of pre-processing
improvements.
|
|
 |
Composite Bridge Deck design
- Composite
Bridge Deck Design facilities now include comprehensive design
checks for Strength/ULS bending stress and interaction effects,
SLS, fatigue, shear connector and stiffener design, based on
stresses built up through the stages of construction and
in-service.
- In addition to an existing supported
code for USA, design checks can now be carried out for AASHTO LRFD
9th Edition (USA), and CSA S6:19 and CSA S6-14
(Canada). For composite bridge
deck design checks to EN1994 (Europe), the Composite
Deck Designer (PontiEC4) software option is available.
- See the full list of design
codes now supported.
|
RC Slab/Wall Design
- The RC Slab / Wall Design
facility now carries out comprehensive design checks to a large
range of international Codes of Practice. It includes Strength/ULS
and SLS checks based on flexural, twisting and in-plane effects,
shear, stress limits, minimum and maximum areas of reinforcement
and crack widths or spacing considerations as appropriate for all
supported codes
- RC Slab / Wall modelling and design
checks are now performed in a similar manner to the way that
RC Frame modelling and design checks are carried out. In
addition to the existing reinforcement attributes, reinforced
concrete material and RC slab / wall design attributes can
now be assigned to surfaces in a model that represent slabs or
walls. A RC Slab / Wall Design results object is used to bring
together loadcases / combinations appropriate to specific design
checks and identify members for which calculations are required.
Results can be viewed either on the model, in tabular format, or
by using the print results wizard.
- In addition to existing supported
codes for USA, Canada, Europe, UK, India, Australia, Singapore and
China, design checks can now be carried out for: AS3600-2018
(Australia), AS5100.5-2017 (Australia), AASHTO LRFD 8th
and 9th Editions (USA), ACI 318-19 and ACI 318-14
(USA), CSA C6-14 and CSA C6:19 (Canada),
JTG3362-2018 (China), ELOT EN 1992-1-1 and ELOT
EN 1992-2 (Greece), NZS 3101-1:2006 and NZTA Bridge
Manual v3.3 (New Zealand), MOMRA Bridge Design (Saudi
Arabia) and SABS 0100-1 (Ed. 2.2) (South Africa).
- A sandwich model has been introduced
based upon Annex LL of EN1992-2. It divides a shell element into
three layers. The outer or cover layers are considered to act as
membranes resisting the direct in-plane forces along with the
resolved forces from the bending and twisting moments. The central
core resists transverse shearing forces only. This model has been
added for AASHTO (USA), AS3600 and AS5100
(Australia), CSA-S6 (Canada), EN1992-2 and GB50010
(China). This major improvement to the RC Slab/Wall design
facility removes most of the limitations of the currently
implemented methods (Wood-Armer and Clark-Nielsen) and
extends the applications for which this facility can be used.
- Detailed rendered calculations
referencing clauses from design codes are now available for all
checks made for all design codes.
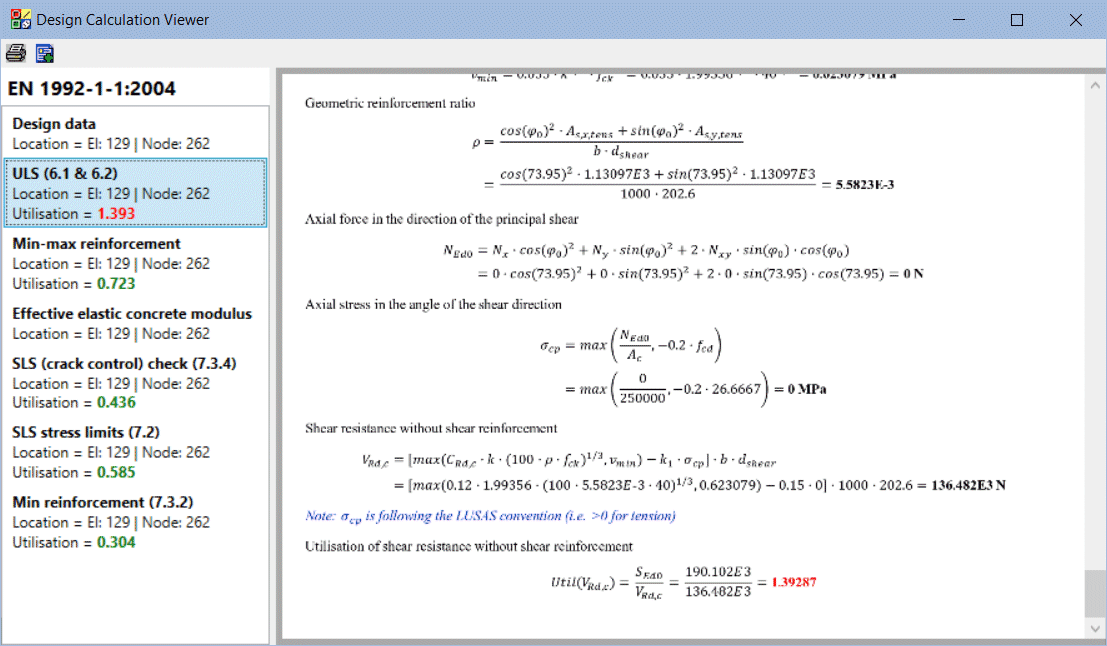
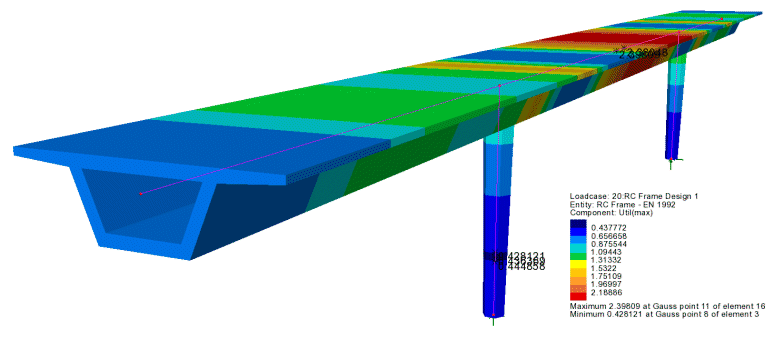
RC Frame Design
- The RC
Frame Design facility now carries out comprehensive design
checks to a range of international Codes of Practice. It includes
Strength/ULS checks based on biaxial bending with overall
tension/compression, shear and torsion, and SLS checks for stress
limits, minimum and maximum areas of reinforcement and crack
widths or spacing considerations as appropriate for all supported
codes, for standard and arbitrary shaped sections and prismatic or
tapering members.
- In addition to existing supported
codes for USA, Canada, Europe, UK, India and Australia, design
checks can now be carried out for AASHTO 9th Edition (USA),
ACI 318-19 (USA) and CSA S6:19 (Canada).
- The existing RC Line Reinforcement
dialog has been extended to allow the specification of
reinforcement for shear acting in local z and local y directions
along with reinforcement considered for resistance to torsion.
- See the full list of RC
frame design codes now supported.
|
|
|
|
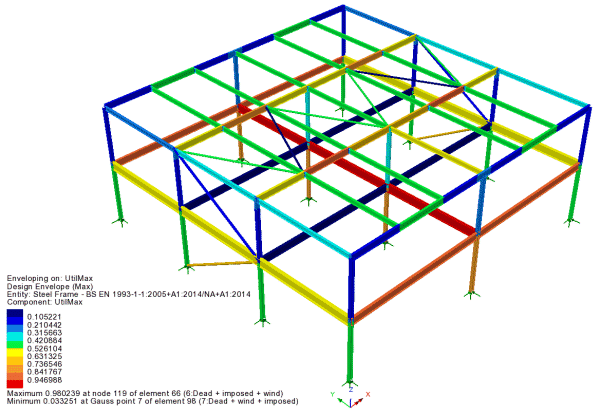
Steel Frame Design
- The Steel
Frame Design facility carries out ULS/Strength checks based on
biaxial bending with overall tension/compression and shear -
including interaction formulae and buckling checks - for a large
range of section profiles and international Codes of Practice.
- In addition to existing supported
codes for USA, Canada, Europe, UK, Australia and China, design
checks can now be carried out for CSA S6:19.
- See the full list of Steel
frame design codes now supported.
|
Concrete Creep and Shrinkage
- The range of concrete creep and
shrinkage material models has been extended to include those for AASHTO
8th and 9th (USA), along with codes covering Europe, China and
India plus both CEB-FIP Model Code 1990 and fib Model
Code 2010.
Prestress
- Time dependent prestress
capabilities have been extended to include those for AASHTO 8th
and 9th Edition along with codes matching the creep and
shrinkage material capabilities.
Vehicle Load Optimisation
- By defining coincident effects of
interest for a Direct Method Influence attribute prior to
running an influence analysis, users of the Vehicle
Load Optimisation facility can now obtain coincident component
effects for the loads that give the most onerous main effect at
locations of interest, without the need to create additional
loadcases and run a static analysis.
Rail Track Analysis
- The Rail
Track Analysis software option has been enhanced to support an
increased number of spans/decks and tracks, and now supports mixed
decks / ballast.
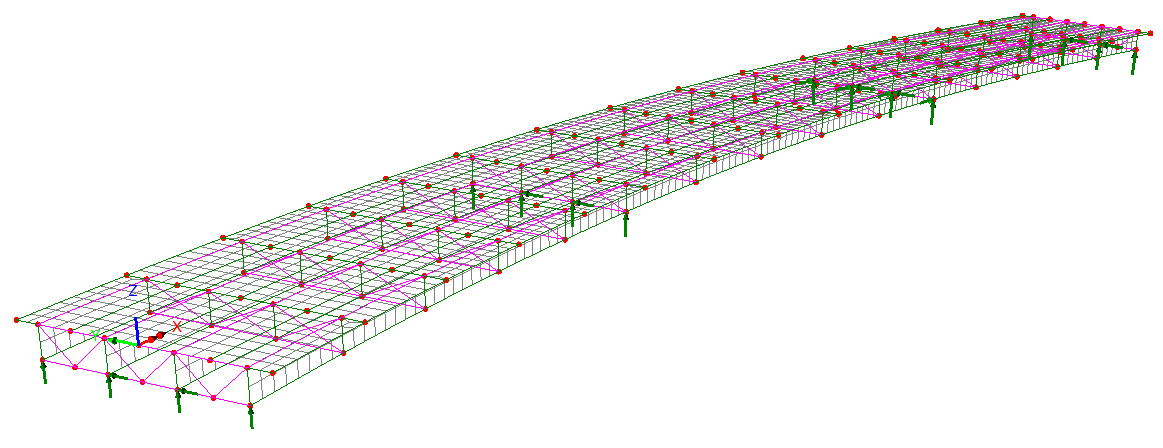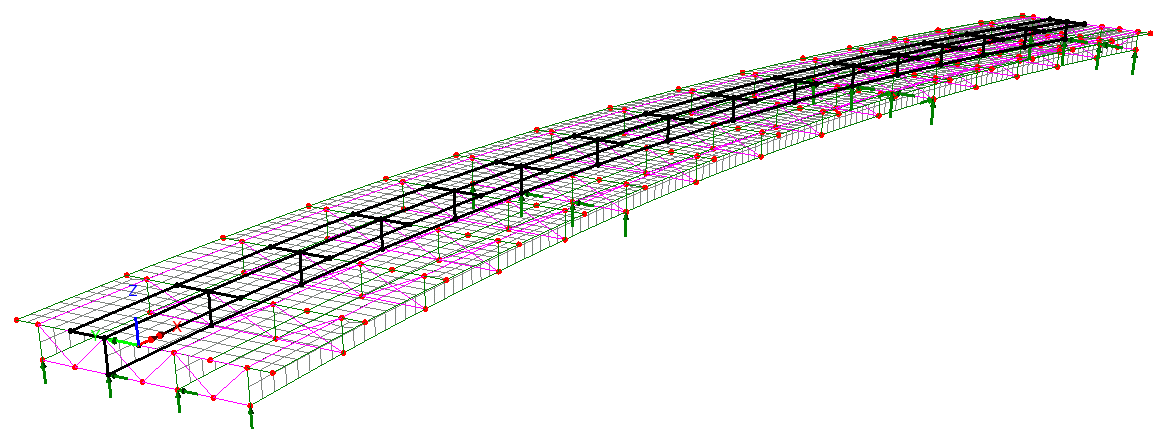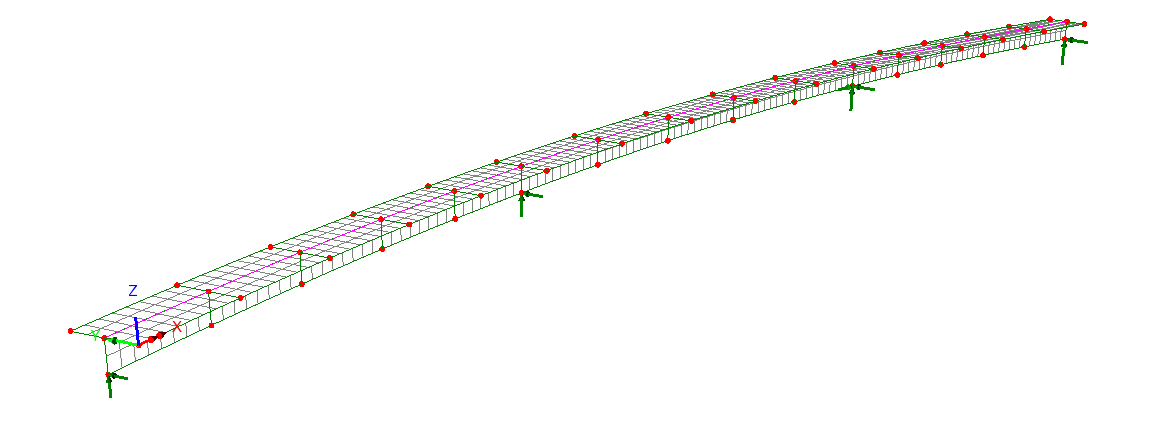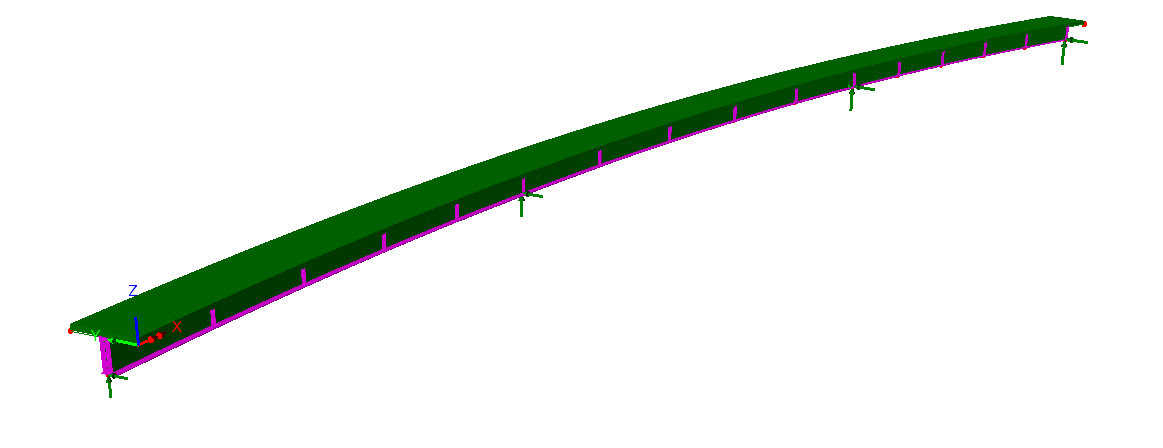
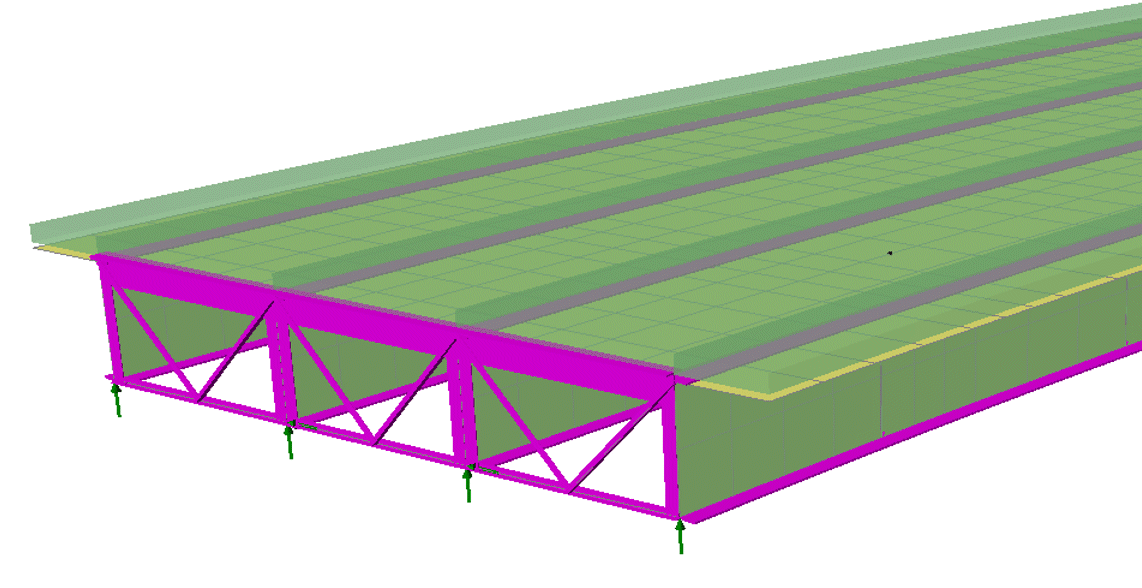
New Bridge Deck (Grillage) attributes
The range of Bridge Deck (Grillage)
geometric attributes based on formulae published by Hambly (and
others) has been extended to include:
- Precast section with concrete
infill, comprising a slab formed of a series of sections from the
section library in a row, surrounded by concrete infill.
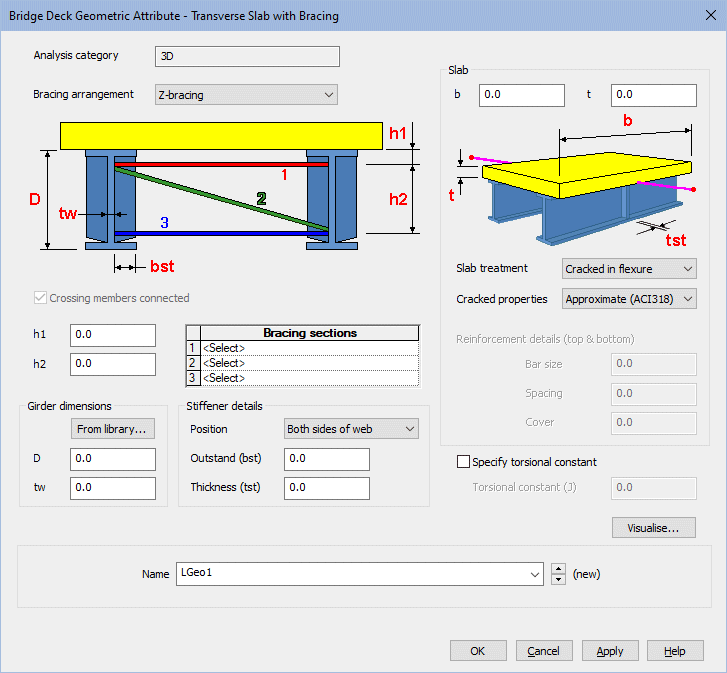
- Transverse slab with bracing with
options of Z-bracing, X-bracing, K-bracing, Lean-on, Single
horizontal, and Torsional.
|
|
|
|
Section property calculation
- User-defined standard and arbitrary
sections are now created and saved within a model file as a model
utility in the Utilities Treeview, rather than in a local or
server-based sections.csv file as in previous versions. These
sections can be defined, either on-the-fly from within the
Attributes > Geometric > Section Library geometric line
dialog, or from the Utilities > Section Property Calculator
menu.
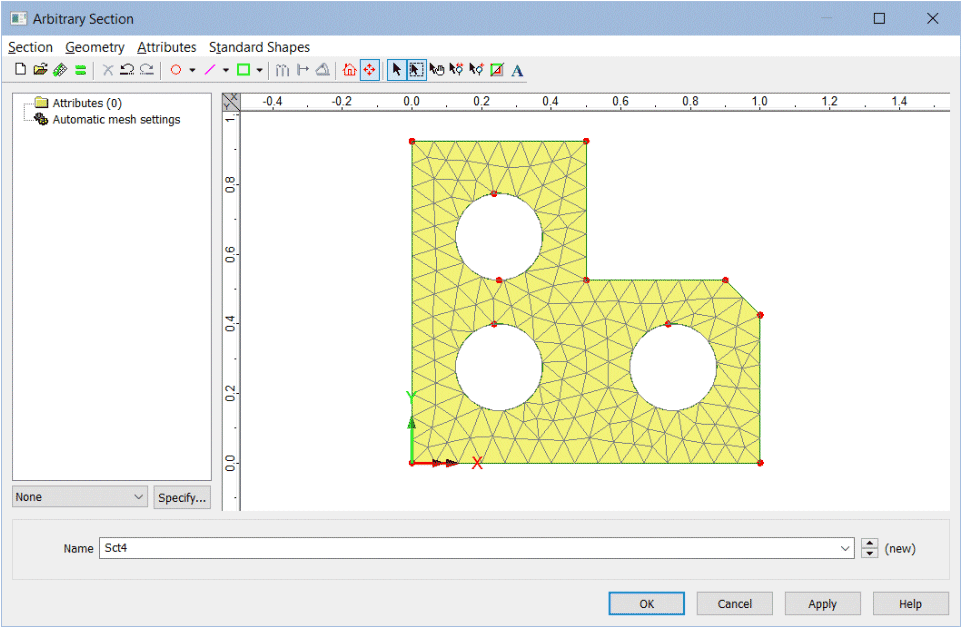
- User-defined arbitrary
cross-sections are now created in a new Arbitrary Section view
window, which contains a reduced set of menu items and toolbar
buttons from the main Modeller window that are suitable for
creating and manipulating these sections.
- Section geometry from standard
library sections/shapes can now be imported into the Arbitrary
Section Property Calculator allowing, for example, a surface
representing a slab to be added to a beam (or beams), or more
complex section shapes to be drawn
- Previously saved LUSAS models
either representing a section, or for use in defining a 2D
cross-section, can be imported for use within the Arbitrary
Section Property Calculator.
- Sections created in the Arbitrary
Section Property Calculator can be exported as a LUSAS model.
|
- When opening pre-version 20 models,
user-defined standard and arbitrary sections referenced by a
geometric beam attribute are automatically converted into model
utilities and will appear in the Utilities Treeview when a
model is loaded.
- A new import sections facility
allows for importing selected sections from any legacy
sections.csv file into the current model. Sections are listed
according to section type with check boxes to allow selection of
any / all sections to be imported into the Utilities
Treeview.
- A new plate section property
calculator calculates properties for a range of riveted or welded
section types, either with reference to sections held in the main
section library or from user-defined values.
- The Precast section menu item has
been removed from the Section Property Calculator menu list.
Precast sections (without a top slab) are now available in
the section library. Precast beam sections with a top slab
can now be created by using the Bridge Deck (Grillage) section
property calculators or, if required, the updated Arbitrary
Section Property Calculator.
Bridge temperature and shrinkage profiles to
design codes
- In addition to existing supported
codes for AASHTO, Australian and Europe, temperature profile
loading to design codes now includes Canada CSA S6-06, S6-14
and S6:19, China JTG D60: 2004 and 2015, India IRC
6 - 2017, New Zealand SP/M/022 Third Edition (Amendment 3,
2018), South Africa TMH 7, UK BD37/01, and UK CS
454 Revision 0.
- Bridge deck shrinkage loading now
includes AASHTO 9th and Canada CSA S6-14 and S6:19
Pile-soil interaction modelling
- A new Embedded pile material layup
attribute provides the means to specify the soil around an
embedded pile in terms of strata, p-y curve data and associated
settings. P-y curves can also be created using the Utilities >
P-y Curve menu item. As in industry, the term "p-y
curve" is used as a shorthand meaning to incorporate p-y
curves, t-z curves and Q-z curves. P-y curves can be defined for a
library of soil materials, namely: API RP2A-WSD, DNV-OS-J101,
ISO 19902:2007 or JTS 167-4-2012.
- A new material model (model 49) has
been introduced for use by the embedded pile material layup which
allows the modelling of load history. Resultant lateral
force-displacement and vertical force-displacement curves describe
the deformation of the pile.
- The existing piecewise linear
elastic joint model dialog now includes a 'Cylindrical' check box
(for the no rotational stiffness joint type), which provides the
option to set force/displacement curves in both vertical and
radial directions, instead of in three Cartesian axes.
|
|
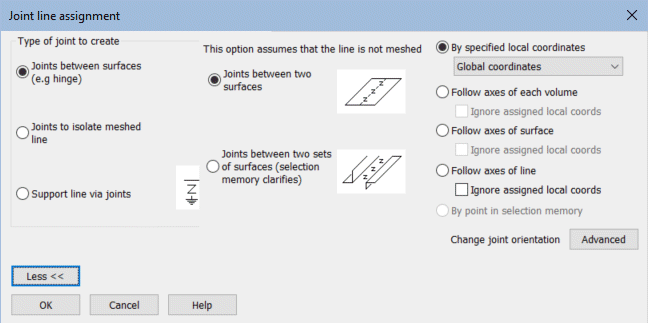
Improved joint and interface assignment
- The insertion of joints or interface
elements has been simplified and automated for specific
situations. Joints can now be inserted by assigning a joint mesh
to features that form the boundary to neighbouring features. This
improved method of inserting joints automatically creates the
required additional nodes and inserts joint elements at nodal
locations at, along or across a selected feature in the case of
points, lines or surfaces. Assignment can be made to a selection
of many single features simultaneously.
- Point, line and surface features can
now be 'grounded' via joints, whereby relevant support conditions
are applied to the free node of the joint element(s)
automatically.
- The offset distance at which a joint
symbol is drawn away from the actual joint location can now be
specified.
- The previous 'manual' method of
inserting joints has been retained for legacy purposes and for
cases not covered by the new 'automatic' method.
|
|
|
|
Enhanced membrane behaviour
- The implementation of corotational
formulation for large deformation of membrane elements now
allows these elements to be used in linear buckling and nonlinear
static and dynamic analysis involving large deformation. This
allows membrane elements to be used in form-finding for tensile
fabric structures, for example.
Evaluation version
- An evaluation version of LUSAS is
now available, requiring registration in order to use an online
evaluation licence.
User interface enhancements
- User-controlled transparency has
been introduced providing clearer and more detailed visual
feedback when modelling and viewing results. Transparency is
supported on a per-layer basis for each view window and also
allows for individual transparency settings for specific geometric
attributes in the Attributes Treeview.
- Updated Attributes Treeview icons
show the status of any defined, assigned or transparent
attribute settings including using individual icons for point,
line, surface and volume based assignments.
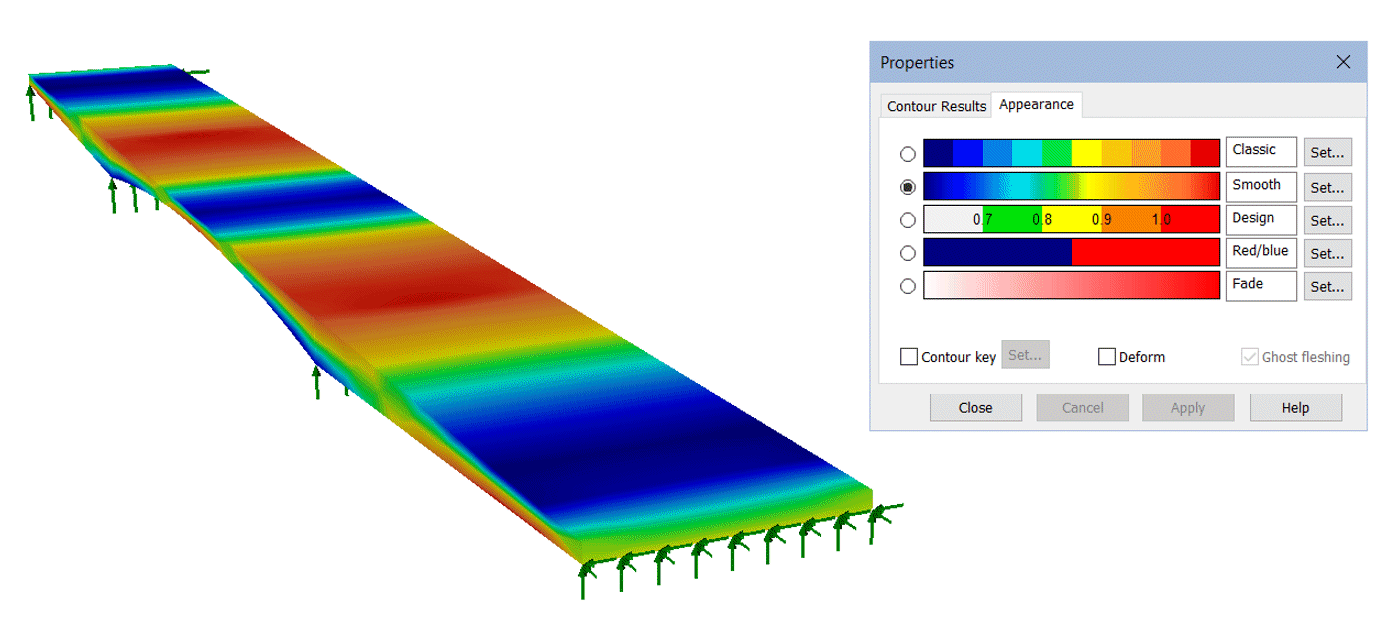
- Improved default contour
appearance. The contour properties dialog has been updated
with the 'Contour Display', 'Contour Range' and 'Seed Colours'
tabs now replaced by one 'Appearance' tab that provides access to
most of the settings from the removed tabs. In addition, five
contour 'styles' can be used as supplied or be customised to plot
contours for different uses in order to suit project needs.
- Two new results components “Stress"
and “Strain" are provided for shell elements. These
allow viewing contours consistently with other results, with
the results to be drawn over the whole "fleshed region"
of each element.
|
 |
|
|
User change requests
The originators of all requested
changes to the software that have been incorporated in this release
will be notified individually.
- Re-ordering of Attributes and
Utilities treeview items. Attributes (and utilities) can now
be clicked and dragged up and down their respective treeviews. As
with loadcases that already support this ability, ID numbers are
updated to suit. In order to force an attribute to be in first
place, it is necessary to drag it on top of its parent item. Note
that reordering is not permitted when attributes are being viewed
in alphabetic order.
- Renumbering of Attributes and
Utilities treeview items. It is now possible to renumber any
group of attributes (and utilities) by right-clicking on the
appropriate folder name and choosing 'Renumber'. Right-clicking on
the Attributes/Utilities folders or in the white space beneath
their respective treeviews allows for renumbering of all
attributes within each parent folder/entry from the same specified
value.
- Filtering of Attributes and
Utilities Treeview data is now possible by selecting either
'None', 'Geometric', 'Material', 'Supports', 'Loading' or 'All'
from the panel at the foot of those treeviews. As implemented
initially for the for the Analyses treeview, this automatically
“closes up” parent folders of all tree branches, and “opens
up” only the desired ones, effectively hiding entries and
reducing clutter. A 'Specify' button can be used to create more
complex permutations – e.g. a selection of 'Loading' and
'Supports'.
- 'Mirror (screen)' option added to
the 'Copy' dialog. This allows users to choose which of the
four extremities of the selection (left, right, top, bottom, in
screen axes) to use as the mirror plane. An extra radio button
allows the further choice of mirroring about a selected /
specified mirror line.
- New 'Threshold' option on the
Values properties dialog.This enables labelling of values
above a specified value. Two new edit boxes for minimum and
maximum thresholds, are provided which are dependent on the
existing “maxima” and “minima” choices.
- Easy stepping through loadcases.
The current active loadcase name is now stated beneath the
Analyses Treeview. Adjacent 'Plus' and 'Minus' buttons, when
chosen, set active the next and previous loadcase within each
Analysis in the Analyses Treeview, allowing stepping through a
series of loadcases to easily view modelling stages or results.
- Reduction of error and warning
messages output. The number of errors and warning messages
from Solver written to the Modeller text output window has been
reduced to a maximum of 5 errors and 25 warnings.
- Filtering of text output. ext
output messages can now be filtered according to type (error,
warning, errors and warnings, etc.) by selection of an appropriate
radio button at the top of the text output window and, for ease of
viewing, symbols have been added to denote the type of message
produced.
- IDs of constituent loads are now
shown in the Compound Load dialog box.
- A checkbox option 'Skip mesh' has
been added to the 'File open' dialog to omit loading the mesh
when a model is loaded. This will allow for faster loading of
large models, if wanting to just check some geometric information
or detail, or to load a model successfully if the mesh has somehow
become corrupted.
- Loadcase definitions can now be
viewed within Combinations and Envelope listings. A new 'View'
button has been added to every dialog where it is possible to
include some loadcases from an 'Available' list into an 'Included'
list, as seen on combination and envelope definitions and
animation load history dialogs. For a selected item in the
'Available' panel, pressing this button opens up the definition
dialog for the item to act as a reminder of the
definition. Where the selected loadcase is a combination or
envelope, the definition dialog will have the same 'View' button,
allowing recursive viewing of the loadcases used in each higher
definition.
Withdrawn facility
The Precast Beam Section Generator
previously provided in Bridge and Civil & Structural software
products has been withdrawn.
- For grillage models, creating a
section comprising a beam (of various types) with or without a
slab is now supported by the Bridge Deck (Grillage)
geometric attribute 'Girder with a top slab' , selecting a precast
beam from the library of those available and defining a slab as
necessary.
- For other applications, the
Arbitrary Section Property Calculator can be used to pull in a
precast beam section from the library and a slab can be added by
defining a rectangular surface to sit on top of the chosen beam
section.
Documentation
User manuals
- All online and printable
documentation has been updated for this new release.
- Selected manuals are provided in PDF
format as part of the LUSAS installation and are also available
for download from the LUSAS website.
Worked Examples
- Worked examples (in PDF format) and associated files referenced by them are no longer installed to a read-only system folder but are instead available for download from the LUSAS
website.
Potential issues
opening PDF files referenced in CHM files
On some PCs, and for certain operating systems,
the installation of security updates as released by Microsoft can
affect the opening of PDF files from the table of contents panel
within the CHM file-based help. Any links to PDF files from within
help topic pages may similarly be affected.
If problems are found when
attempting to open these files from within the online CHM file
supplied please note the following:
- Selected manuals
are supplied in PDF format on the installation kit and these are
normally installed into the <LUSAS Installation
Folder>/Programs/PDF_Manuals folder.
- Workarounds/solutions
may be provided by Microsoft during the availability and support
of this particular LUSAS software release.
|

















