Software Option for Bridge plus
and Civil & Structural plus versions
Geotechnical Analysis
Unlike some structural analysis
software,
LUSAS Civil & Structural plus and LUSAS Bridge
plus software products when used with appropriate geotechnical,
nonlinear, dynamic and thermal/field software options, provide a range
of soils-specific and general structural engineering analysis tools to
enable finite element modelling in 2D or 3D of both ground and
structure in a single model.
Multiple analyses can
be solved within each model, and state-of-the-art linear and quadratic
element libraries; advanced material models; and linear and nonlinear
joint models allow a range of soil-structure engineering problems to
be solved

| Available
without use of the Geotechnical option |
Available
with use of the Geotechnical option |
Geotechnical facilities available in LUSAS Civil & Structural plus and LUSAS Bridge plus software:
- Soil-structure interaction modelling using 2D/3D springs
- Tresca material model
- Trilinear earth pressure joint modelling
- Embedded pile material layups
- P-y curves, t-z curves and Q-z curves.
- Reset deformation capability to model the undisturbed ground shape, while incorporating the stress distribution appropriate to the pre-existing equilibrium with geostatic loads.
|
All capabilities listed in the adjacent column for LUSAS Civil & Structural plus and LUSAS Bridge plus software and in addition:
- Soil modelling using 2D/3D continuum elements
- Duncan-Chang, Hoek-Brown, Modfied Cam-Clay, Mohr-Coulomb, Modified Mohr-Coulomb, Drucker-Prager, Tresca, Interface materials for Mohr-Coulomb Friction Interface and Elasto-plastic Interface material models.
- Two-phase material properties
- Phi-c reduction (for Mohr-Coulomb and Hoek-Brown models)
- Ko initialisation
- Pore water pressure modelling for drained, undrained and phreatic surfaces
- Drainage / filling curves
- Water pressure distribution loading
- Pore pressure flux loading
- Pore pressure supports - open, closed, seepage, drainage
- Non-reflecting / absorbing boundaries
- Viscous support loading for use with non-reflecting / absorbing supports in the model
|
Modelling
-
LUSAS models are
created using feature-based geometry methods (points, lines,
surfaces and volumes) and built-in associativity, a key feature of
the LUSAS Modeller, ensures that if the model geometry is amended,
all assigned loadings, supports, mesh and other attributes are
automatically updated to suit.
CAD import /
export facilities permit importing of point and line data from DXF
files; points, lines, surfaces and volumes via IGES/STEP
interafaces; and triangulated surface data through STL. CAD-style
drawing tools provide an array of modelling utilities such as copy,
rotate, scale, transform, extrude etc.
For 2D
modelling splines can be created from terrain points data and swept
to create strata. Surfaces can be defined from bounding points and
lines, and swept to define a soil mass. Structural and soil
components can be grouped for modelling purposes. For 3D modelling,
planar or curved surfaces can be swept for multiple volume creation,
and intersection and subtraction commands provide the means to slice
volumes or create voids.
Automatic 2D
meshing (using quadrilateral/triangular elements) and 3D meshing
(using tetrahedral/pentahedral/hexahedral elements) speeds up the
modelling process. Various mesh refinement methods are provided.
-
Calculate
initial stress states providing K0
data and apply to any ground profile.
-
Constitutive soils
models include Mohr Coulomb, Modified Cam Clay, Tresca, Von Mises,
Drucker Prager, Duncan-Chang, Hoek-Brown.
-
Two-phase material
properties can be added to selected materials to permit modelling
the deformation of undrained/fully saturated and
fully-drained/unsaturated porous media, and slow consolidation
process. Draining and filling curves can also be specified for
partially drained materials.
Define phreatic
surface levels to determine pore water pressures where the water
table is known. Determine levels and pressures between those
locations based on porosity and hydraulic conductivity.
Alternatively define pore pressures based on piezometer readings
or borehole data.
Model the variation
of soil properties with depth by defining soil profile variations,
with LUSAS interpolating between defined locations.
Nonlinear springs
model active/passive soil joints. Interface meshes permit joining
of the soil / structure. Gain / loss of contact, and skin friction
can be considered.
Specify a matrix of
properties to represent a pilecap sitting on a group of piles in a
3D model.
A Tri-linear
(active/passive) earth pressure joint material wizard simplifies the
modelling of a variety of soil-structure interaction problems,
creating a piecewise linear joint material attribute with properties
that vary with depth. Multiple attributes can be defined to
represent layers of soil or changes in properties due to the
presence of water.
Use a Phi-c
reduction analysis to assess soil stability and safety factors for
soil represented by Mohr-Coulomb or Hoek-Brown material models.
Use time dependent
loading for impact or time history and use non-reflective
boundaries to transfer energy out of the sub-model for realistic
modelling of response and interference.
Use branched
analyses to study safety factors at several stages of construction
without terminating the solution.
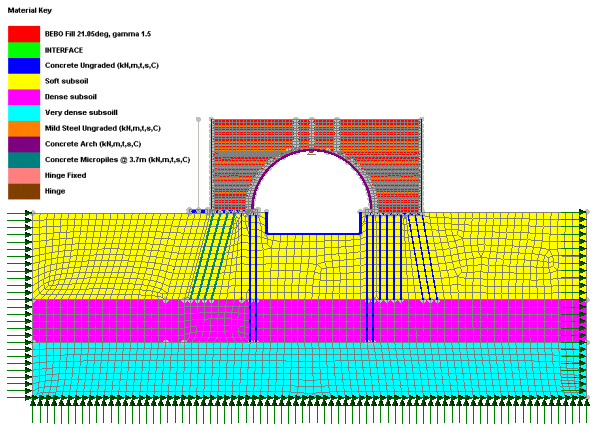
Typical applications
LUSAS is used in all
areas of civil, structural and bridge engineering for linear,
nonlinear, seismic, blast, buckling, impact and thermal/field
analysis. It can be used on all types of structures from simple slabs,
buildings, towers, tanks and bridges through to heavy civil
engineering structures such as dams, docks and tunnels. General
geotechnical
and soil-structure interaction capabilities include:
-
Construction
sequence modelling - involving excavation / construction with
insertion and removal of temporary members used for propping and
jacking etc.
-
Embankment /slope
stability assessments and stability checks on adjacent structures
due to temporary excavation.
-
Backfilling of
excavations and cut and cover tunnel structures.
-
Settlement and
consolidation including pore water pressure modelling.
-
Dewatering and
seepage modelling of partially saturated fluid flow through porous
media, such as seepage of water through an earth dam, where the
position of the phreatic surface is of interest.
-
Modal and time
history dynamics involving material damping, nonlinear behaviour,
soil plasticity, boundary behaviour and springs/dampers.
-
Soil-structure
interaction analysis including vibration analysis from pile
driving impact assessments on nearby buildings and response of
buildings to emitted vibrations from rail tunnels.
-
Lateral displacement
analysis of piles and pile groups
-
Integral bridges
Dependent software options
Use of the Geotechnical software option
will require one or more of the following other software options to be
accessible, depending upon the modelling to be carried out..
Find out more
|
|
Software Information
|